In Consulting LLC analyzes and identifies samples of unknown composition. Identification and analysis make it possible to determine the origin, qualitative and quantitative chemical composition of the sample, its physicochemical properties, and in some cases, the formulation and production method. Such studies are necessary when the origin of the sample or its composition is unknown. But more often the “analysis” of the chemical composition of the sample is required in other cases: when the data specified in the sample passport is insufficient or there are doubts about the accuracy and correctness of the given data, when it is necessary to restore the sample production technology, check the presence of the main component in the sample or its purity.
Complete chemical analysis
There is also the concept of "complete chemical analysis" in the world. If we mean by this the identification and quantification of absolutely all substances present in the sample, then the task may not be feasible. Technical liquids, samples containing contaminants, or even ordinary tap water are multicomponent mixtures, the number of compounds in which can actually number in the hundreds. But the important point is that the properties of an object, as a rule, do not depend on absolutely all substances that make up its composition, but are determined only by the main components. Sometimes it is not even necessary to investigate in detail the impurities, it is enough to determine their type or nature of origin.
In order to somehow resolve the issues of chemical and physicochemical analysis at the documentary level, there is regulatory documentation. For common objects, there are documented DSTU or TU, which the object must comply with. These documents set out a set of parameters that need to be examined in order to determine the quality of the sample. For objects of economic use, for example, drinking water or food products, there are SanPiN standards, which indicate a list of substances subject to control. Therefore, for all of the above objects, the concept of "complete chemical analysis" can be used to designate the list of chemical and physicochemical studies that must be carried out in accordance with the regulatory documentation.
Some questions that can be answered by chemical analysis of the composition:
- What is the main component of the sample?
- Does the sample match the declared chemical composition?
- What impurities are in the sample?
- Does the amount of impurities meet the permissible standards?
- Does the sample contain toxic substances?
For which objects a chemical analysis of the composition is required:
- Construction chemistry
- Process fluids
- Some polymer compositions
- Chemical raw materials and reagents
- Flavors
- Medicines
- Pure organic compounds
- Industrial products and production waste
When is it not necessary to carry out a complete chemical analysis of the composition?
There are a number of cases when it is not necessary to spend time and resources on determining the composition of the sample, but it is necessary to determine the important parameters of the sample (chemical and / or physical properties). Sometimes it makes sense to measure only these parameters (and not to determine the entire composition). Therefore, it is extremely important to determine the goal before starting the research!
Our approach to chemical analysis of objects of unknown composition
There are several basic conditions for the successful solution of the problem of qualitative analysis and identification:
- The ultimate goal of the study should be clearly stated.
- It is necessary to have a basic understanding of the composition of the investigated object, its nature and origin. Therefore, as in the case of a lawyer and a doctor, the more information you post, the more adequate answers you will receive, since you are not able to set the task yourself due to the lack of specialized knowledge or experience.
- The limits of analytical methods must be taken into account.
- It is necessary to understand that for complex objects it is impossible to guarantee one hundred percent success. But it is always possible to obtain valuable information that will help in the further solution of the problem.
Our strengths in investigating objects of unknown composition
Laboratories of In Consulting LLC have many research capabilities for analyzing the composition of a wide variety of objects. But it is very important in each specific case to correctly determine the goal and draw up a clear research program in order to avoid unreasonable waste of resources. It is the qualified personnel that makes it possible to draw up the most effective research program.
As a rule, the analysis of objects of unknown composition must begin with the classification of the sample and the determination of the range of substances included in its basis. If the origin of the sample is known, then its classification and determination of the basis is not particularly difficult. Otherwise, it is first necessary to carry out preliminary studies in order to answer the main question - is it possible, in principle, to obtain the information about the sample necessary for the customer and whether we will undertake this study.
How much does a complete chemical analysis of the composition cost?
The cost of researching objects of unknown composition varies depending on the objectives of the research. Based on the frequent inquiries of our customers, several research service packages have been developed that allow us to evaluate the cost-effectiveness of determining the chemical composition.
Package «Identification of an unknown substance: inorganic»
| Service (for 1 sample) | Deadlines | Price without VAT* |
| X-ray fluorescence spectrometry (XRF) | up to 4 days | 074 USD |
| Powder X-ray diffraction (XRD) | up to 14 days | 0197 USD |
| TOTAL | up to 14 days | from 271 USD |
The prices are approved by the director of LLC "In Consulting" 13.03.2026. Deadlines are indicated in working days
Package «Identification of an unknown substance: organic»
| Service (for 1 sample) | Deadlines | Price without VAT* |
| Infrared spectroscopy (Fourier-IR, FTIR) | up to 14 days | 0241 USD |
| Raman spectroscopy (Raman) | up to 7 days | 0133 USD |
| Gas chromatography with mass spectrometry (GC-MS) | up to 14 days | 0324 USD |
| TOTAL | up to 14 days | from 584 USD |
The prices are approved by the director of LLC "In Consulting" 13.03.2026. Deadlines are indicated in working days
The cost of packages shows the minimum cost of research at the date of publication of the material. Actual prices are taken according to the current price list .
The choice of a specific package depends on the task at hand, sometimes it is enough to determine the concentration of the main active ingredient. But if the object consists of organic and inorganic substances, then a set of methods is applied.
The final cost of research will depend on the set of substances and the complexity of the analysis methods used.
How is the identification of the chemical composition
The customer is required to provide a sample (from 200 mg to 500 g) and, if possible, all available information about it. And also, explain why the research is necessary and what result is required. Laboratory specialists, in turn, develop sample preparation procedures appropriate for each specific object and select suitable analytical methods. Methods are selected depending on the physicochemical properties of the sample, its ability to dissolve, chemical reactions, etc. Some basic methods of analysis are shown in the figure below.
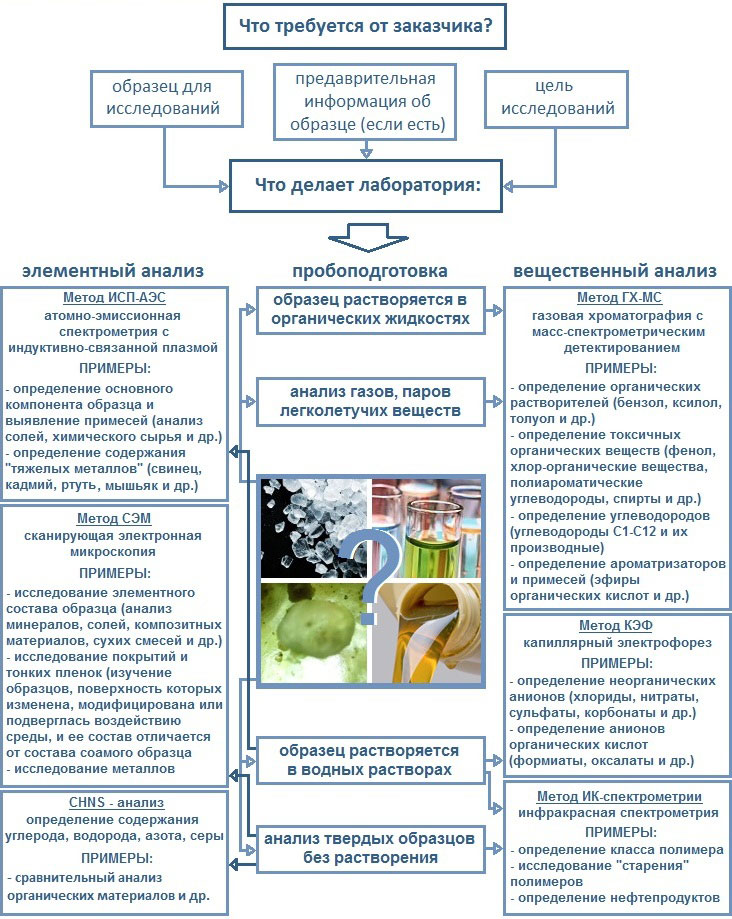
Qualitative and quantitative chemical analysis of the composition
Analysis can have the following tasks:
- establish the approximate nature of the substance (salt, oxide, metal, alloy, etc.);
- detect impurities of other substances in a known substance;
- establish the composition of the unknown substance.
Chemical analysis of objects of unknown composition can be divided into two stages: qualitative chemical analysis (determination of the set of substances that make up the sample) and quantitative chemical analysis (determination of the concentration of each substance present in the sample).
Qualitative analysis allows you to identify the substances present in the sample, that is, to answer the question "what does the sample contain?"
When establishing its composition, an unknown substance can be acids, oxides, salts (medium, acidic, double, mixed, basic), metals, alloys, non-metals, ores, rocks, etc. When establishing the qualitative composition of the listed substances, there is a general approach to conducting a qualitative chemical analysis.
Two cases are possible:
1. The test substance is an individual substance: metal or non-metal, any salt (simple, complex or complex), oxide, hydroxide, acid, etc. An individual substance can be chemically pure or contain small impurities.
Determination of the chemical composition of an individual substance using a qualitative analysis has some peculiarities and differs from the analysis of a mixture of substances.
In the case when the chemical formula of the analyzed individual substance is unknown, then the qualitative composition of the analyte is established by analysis. If the chemical formula of the analyte is known, then its analysis is reduced to establishing the presence of impurities in the analyte. In other words, the purpose of a qualitative analysis of a known individual substance is to determine the degree of its purity.
2. The analyte is an alloy or a mixture of salts, oxides, hydroxides, acids.
Quantitative analysis involves answering the question "how much of a given substance is in a sample?"
Quantitative analysis may require preliminary isolation of the analyte from the sample, its concentration, conversion into the analyte form by chemical reactions, etc. In addition, a detailed selection of conditions and calibration of the device according to a standard sample of a given substance are usually required.
Therefore, the stages of qualitative and quantitative analysis are separated from each other.
For a free consultation, you can use On-line consultation, or call us or write to the messengers.For information about the cost of services go to Tariffs or place Application for Services.









































